Health
Dog Gland Removal Pros and Cons: Everything You Need to Know
As a responsible pet owner, your dog’s health and wellness should be one of your top priorities. One common issue that many dog owners face is anal gland problems. One common issue that many dog owners face is anal gland problems. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive into the Dog Gland Removal Pros and Cons, answer frequently asked questions, and provide expert advice to help you make informed decisions for your canine companion.
Table of Contents
What are Anal Glands and their Functions in Dogs?
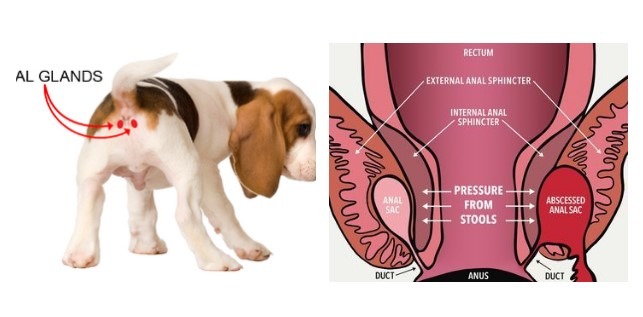
Anal glands, also known as scent glands, are small sacs located on either side of a dog’s anus. They secrete a foul-smelling substance that helps dogs mark their territory and communicate with other dogs. In a healthy dog, these glands are naturally expressed during defecation. However, some dogs may experience problems with their anal glands, such as impaction, infection, or even abscesses. In these cases, a veterinarian may recommend anal gland removal surgery, known as an anal sacculectomy.
Signs that Your Dog Needs Anal Gland Expression
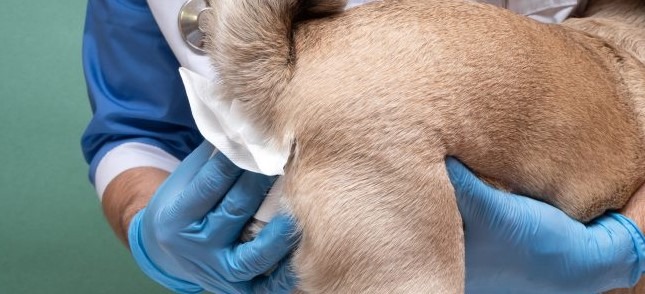
If your dog is experiencing any of the following symptoms, it may be an indication that they need anal gland expression:
- Scooting or dragging their rear end across the floor
- Licking or biting at the area around the anus
- Swelling or redness around the anus
- Pain or discomfort while defecating
- Foul odor near the rear end
If you notice any of these signs, consult with your veterinarian for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Pros of Anal Gland Removal in Dogs
Anal gland removal can provide numerous benefits for dogs suffering from chronic anal gland issues. Some of the pros include:
- Permanent Solution: For dogs with recurring anal gland problems, removal can provide a permanent solution, eliminating the need for regular expressions and reducing the risk of future complications.
- Pain Relief: Dogs with impacted or infected anal glands can experience significant discomfort. Removal can provide immediate relief and improve your dog’s overall quality of life.
- Reduced Risk of Infection: By removing the anal glands, the risk of infection and abscesses is significantly reduced.
- Cost-effective: While the upfront cost of surgery may be high, it can save money in the long run by eliminating the need for ongoing anal gland expressions and treatments.
Cons and Risks of Anal Gland Removal in Dogs
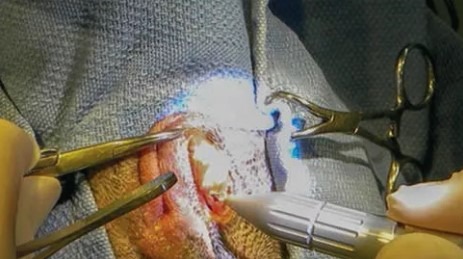
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and cons associated with anal gland removal:
- Anesthesia Risks: Anesthesia carries risks, especially for older dogs or those with pre-existing health conditions. Discuss these risks with your veterinarian before opting for surgery.
- Infection and Complications: As with any surgery, there’s a risk of post-operative infection, bleeding, or complications. Proper post-surgery care and monitoring are essential to minimize these risks.
- Loss of Scent Communication: Although the removal of anal glands eliminates the problems associated with them, it also means that your dog will lose its ability to communicate through scent marking. This may affect their social interactions with other dogs.
- Cost of Surgery: The cost of anal gland removal can be significant, depending on your location and the complexity of the procedure. Pet insurance may cover part of the expenses, but it’s essential to consider the financial impact before proceeding.
Alternatives to Anal Gland Removal in Dogs
Before considering surgery, it’s essential to explore alternative treatments and management options for your dog’s anal gland problems. These may include:
- Regular Anal Gland Expression: Many dogs with chronic anal gland issues can benefit from regular expressions performed by a veterinarian or a trained professional. This can help prevent impaction and reduce the risk of infection.
- Dietary Changes: Adjusting your dog’s diet to include more fiber can help promote firmer stools, which can naturally express the anal glands during defecation. Consult with your veterinarian for dietary recommendations specific to your dog’s needs.
- Anti-inflammatory Medication: In some cases, anti-inflammatory medication can be prescribed to help reduce inflammation and discomfort associated with anal gland problems.
- Antibiotics: If an infection is present, your veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics to treat it and prevent further complications.
Always discuss these alternatives with your veterinarian to determine the most suitable course of action for your dog’s specific situation.
Post-Surgery Care and Recovery for Dogs
If you decide to proceed with anal gland removal surgery for your dog, it’s crucial to follow your veterinarian’s post-surgery care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery. Some tips include:
- Pain Management: Your veterinarian will likely prescribe pain medication to keep your dog comfortable during the recovery process. Ensure you administer the medication as instructed and monitor your dog for any signs of discomfort.
- Wound Care: Keep the surgical site clean and dry. Check for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge. If you notice anything concerning, contact your veterinarian immediately.
- Restricted Activity: Limit your dog’s activity for the first few days following surgery to allow for proper healing. Avoid any rough play, jumping, or running.
- E-Collar: Your dog may need to wear an Elizabethan collar (also known as an “e-collar” or “cone”) to prevent them from licking or biting at the surgical site.
- Follow-up Visits: Schedule follow-up visits with your veterinarian to monitor your dog’s healing progress and remove any sutures, if necessary.
Preventing Anal Gland Problems in Dogs
While not all anal gland issues can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of problems occurring in your dog:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Provide your dog with a well-balanced, high-quality diet that includes an appropriate amount of fiber to promote healthy bowel movements.
- Regular Veterinary Checkups: Schedule regular checkups with your veterinarian to monitor your dog’s overall health and catch any potential issues early.
- Weight Management: Obesity can contribute to anal gland problems, so ensure your dog maintains a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise.
- Grooming: Regular grooming can help keep the area around your dog’s anus clean and reduce the risk of infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How much does it cost to remove anal glands in dogs?
A: The cost of anal gland removal in dogs can vary depending on factors such as your location, the veterinarian’s fees, and the complexity of the procedure. On average, the cost can range from $300 to $1,000. It’s essential to discuss the cost with your veterinarian and explore any financial assistance or pet insurance options available.
Q: What are the risks of not removing a dog’s anal glands?
A: If your dog is experiencing chronic anal gland problems and alternative treatments are not effective, the risks of not removing the anal glands can include recurring infections, abscesses, impactions, and ongoing pain and discomfort for your dog.
Q: How long does it take for a dog to recover from anal gland removal surgery?
A: Recovery time can vary depending on the individual dog and the specifics of the surgery. Generally, most dogs recover within 1 to 2 weeks following anal gland removal surgery. It’s essential to follow your veterinarian’s post-operative care instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.
Q: What should I expect after my dog has anal gland removal surgery?
A: After surgery, your dog may experience some pain, swelling, and discomfort around the surgical site. Your veterinarian will provide you with pain medication and post-operative care instructions to help manage these symptoms. It’s crucial to monitor your dog’s healing progress, limit their activity, and follow up with your veterinarian as needed.
Q: How often should I have my dog’s anal glands expressed?
A: The frequency of anal gland expression varies depending on your dog’s specific needs. Some dogs may require expression as often as every few weeks, while others may only need it once or twice a year. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate frequency for your dog.
Q: What are the long-term effects of anal gland removal in dogs?
A: Long-term effects of anal gland removal in dogs are generally positive, with most dogs experiencing relief from chronic anal gland problems. However, it’s important to note that dogs will lose their ability to communicate through scent marking, which may affect their social interactions with other dogs.
Q: Can anal gland problems in dogs be prevented?
A: While not all anal gland issues can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of problems occurring in your dog, such as maintaining a healthy diet, ensuring regular veterinary checkups, managing your dog’s weight, and keeping up with regular grooming.
Also Read: Smoking Lavender: Pros and Cons Explained
Conclusion
In conclusion, dog gland removal can be a beneficial solution for dogs suffering from chronic anal gland problems. However, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons, explore alternative treatments, and consult with your veterinarian to make the best decision for your dog’s health and well-being. By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure your dog lives a happy, healthy life.

-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoAdvantages and Disadvantages of Milk
-

 Tech4 years ago
Tech4 years ago6 Tips to Improving E-Commerce Websites
-

 Home5 years ago
Home5 years agoAdvantages and Disadvantages of Village Life in Points
-

 Travel5 years ago
Travel5 years agoAdvantages and Disadvantage of Travelling
-

 Sports3 years ago
Sports3 years agoThe benefits of playing an online live casino
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years ago10+ Advantages and Disadvantages of Mobile Phones in Points
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years agoEssay on Advantages and Disadvantages of Offline Shopping
-

 Tech5 years ago
Tech5 years ago8+ Advantages and Disadvantages of Motorcycle |Having Bike